This is not the current version. View the latest documentation
Getting started
Please note that we do not support Java outside of Android at the moment.
Prerequisites
- Android Studio (>= 0.8.6) — to use Realm from Eclipse, see below.
- A recent version of the Android SDK
- JDK version >=7.
We support all Android versions since API Level 9 (Android 2.3 Gingerbread & above).
Installation
You can either use Maven or manually add a Jar to your project.
Maven
- Make sure your project uses jcenter as a dependency repository (default on latest version of the Android Gradle plugin)
- Add
compile 'io.realm:realm-android:0.72.0'to the dependencies of your project - In the Android Studio menu: Tools->Android->Sync Project with Gradle Files
Jar
- Download the release package and unzip.
- Create a new project with Android Studio
- Copy the
realm-VERSION.jarfolder intoapp/libs - In the Android Studio menu: Tools->Android->Sync Project with Gradle Files
- From Eclipse select “Help” -> “Install New Software” and install “Eclipse Java Development Tools”
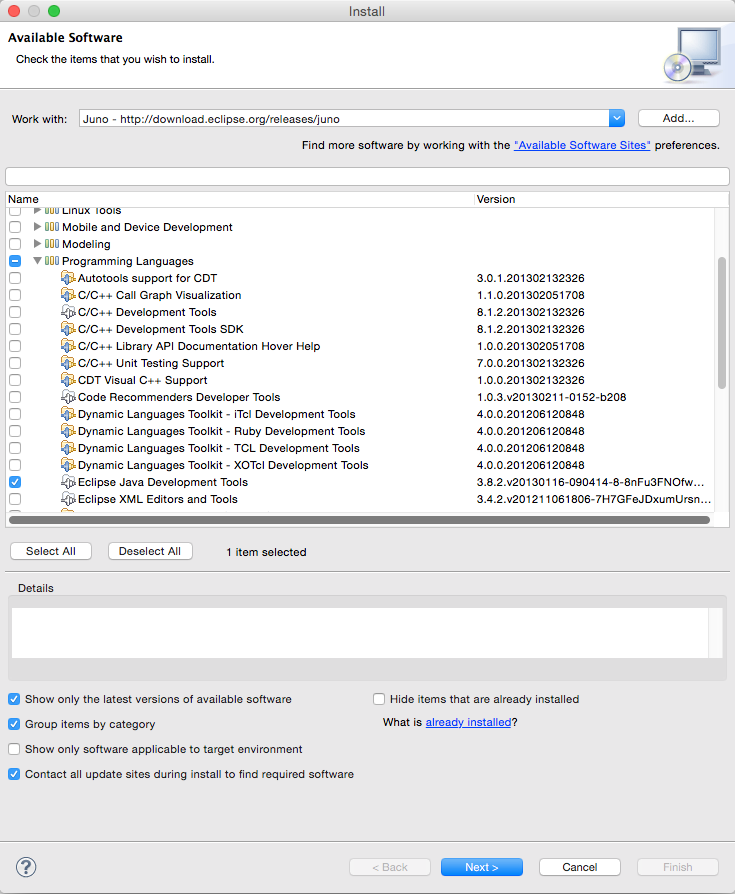
- Download or clone the source of realm-java locally.
-
From the root of the source, build the distribution files:
sh ./build-distribution.sh - Copy the jar file and folders (containing the
libtightdb-jni.sofiles) fromdistribution/eclipse/to your app’slibsfolder. - Right click on the realm jar file from
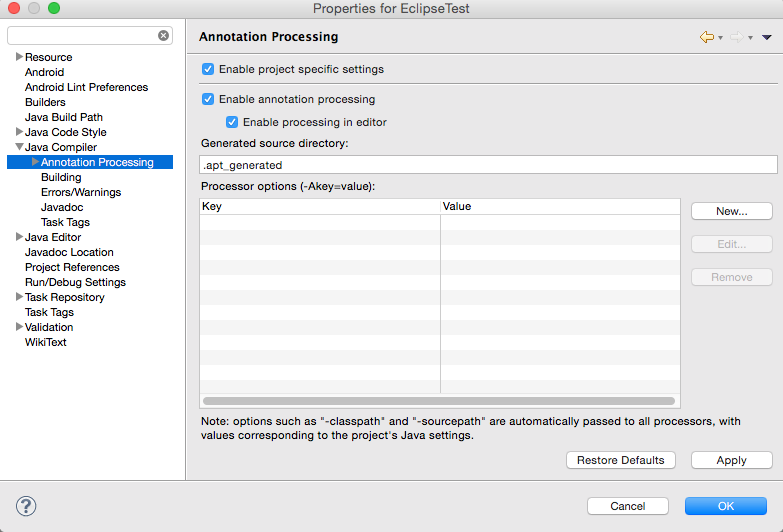
libsfolder, and go to “Build Path” -> “Add to Build path”. - Right click your project and select “Properties”, go to “Java Compiler” -> “Annotation Processing”, check “Enable project specific settings” and then click “Apply”.
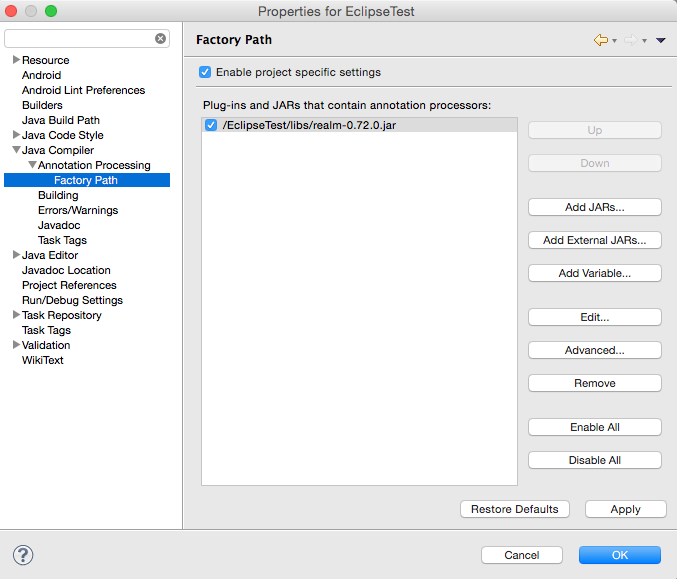
- Continue to “Annotation Processing” -> “Factory Path” and check “Enable project specific settings”. “Click Add JARs” and select the realm jar file in “libs”, click OK, Apply and finally build.
- In order to trigger the annotation process, you must add the annotation
@RealmClassbefore every one of your RealmObject subclasses.
Realm Browser
Only available on Mac OS X at the moment! We are working on Windows & Linux versions.
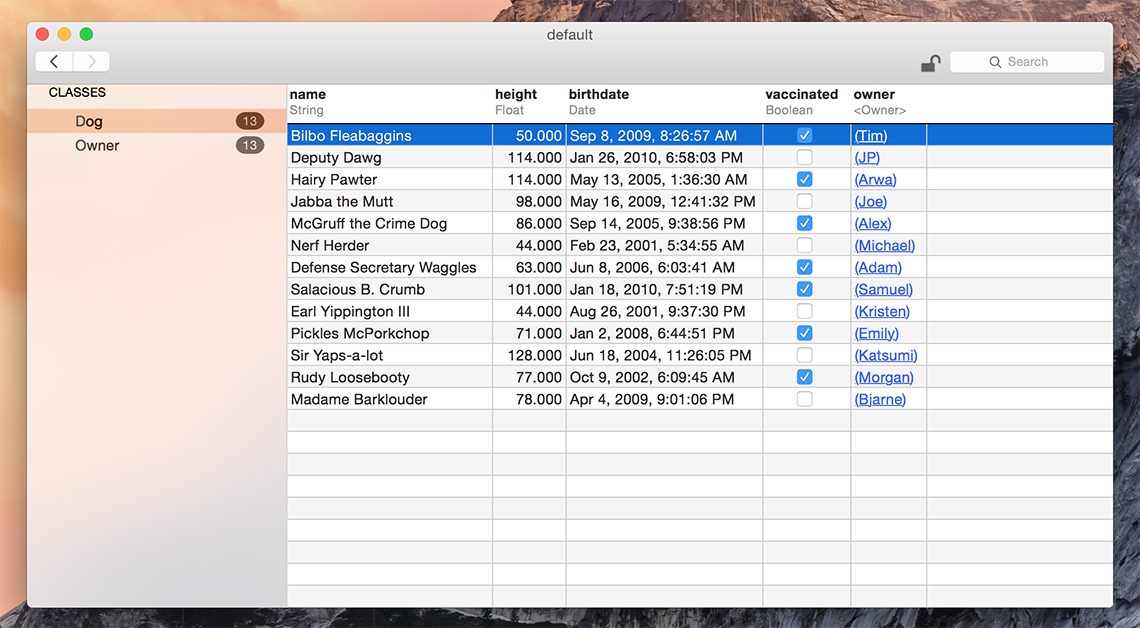
We also provide a standalone app to read and edit .realm databases.
You can find it in our Cocoa release zip under browser/.
You can generate a test database with dummy data using the menu item Tools > Generate demo database.
Examples
The root folder contains a few examples to get you started. You just Import Project in Android Studio and hit run.
The RealmIntroExample in the root folder contains simple examples of how you use the current API. Checkout the source code, as you will only see little output in the Log.
The RealmGridViewExample is a trivial app that shows how to use Realm as the backing store for a GridView. It also shows how you could populate the database with JSON.
The RealmConcurrencyExample is a simple app that shows how to use Realm in a multithreaded environment. You will be able to do write operations from the UI but the most interesting bits are hidden in the code so take a dive and explore it!
Getting Help
- Sign up for our community newsletter to get regular tips, learn about other use-cases and get alerted of blogposts and tutorials about Realm.
- We rely on you to send your questions, as well as your candid feedback to help shape Realm for Android! Please direct all questions and feature requests to realm-java@googlegroups.com.
- While we discourage using it for help/debugging of your app (which is better done on the Google Group), we highly encourage all bug reports to be filed directly as issues on our GitHub repo!
Models
Realm data models are defined by implementing something very similar to a traditional Java Bean. Simply extend our RealmObject and let the Realm annotations processor generate proxy classes.
public class User extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private int age;
@Ignore
private int sessionId;
// Standard getters & setters generated by your IDE…
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
public int getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
public int getSessionId() { return sessionId; }
public void setSessionId(int sessionId) { this.sessionId = sessionId; }
}Be aware that the getters and setters will be overriden by the generated proxy class used in the back by RealmObjects, so any custom logic you add to the getters & setters will not actually be executed.
RealmObjects are strongly tied to one Realm so they must be instantiated from the Realm using the realm.createObject() instance method.
Field types
Realm supports the following field types: boolean, short, int, long, float, double, String, Date and byte[]. The integer types short, int, and long are all mapped to the same type (long actually) within the realm. Moreover, subclasses of RealmObject and RealmList<? extends RealmObject> are supported to model relationships.
Ignoring properties
The annotation @Ignore implies that a field should not be persisted to disk. Ignored fields are useful if your input contains more fields than your model, and you don’t wish to have many special cases for handling these unused data fields.
Search index
The annotation @Index will add a search index to the field. This will make inserts slower and the data file larger but queries will be faster. So it’s recommended to only add index when queries need to be faster. Only string fields can currently be indexed (other types will be supported in future release), and it is not possible to remove a search index.
Writes
Read operations are implicit which means that objects can be accessed and queries at any time. All write operations (adding, modifying, and removing objects) must be wrapped in write transactions. A write transaction can either be committed or cancelled. During the commit, all changes will be written to disk, and the commit will only succeed if all changes can be persisted. By cancelling a write transaction, all changes will be discarded. Using write transactions, your data will always be in a consistent state.
Write transactions are also used to ensure thread safety:
// Obtain a Realm instance
Realm realm = Realm.getInstance(this);
realm.beginTransaction();
//... add or update objects here ...
realm.commitTransaction();Because objects are strongly tied to a Realm, they should be instantiated through the Realm directly:
realm.beginTransaction();
User user = realm.createObject(User.class); // Create a new object
user.setName("John");
user.setEmail("john@corporation.com");
realm.commitTransaction();Since you must create an object within a realm before filling in the data, you might end up in a situation where you wish to discard a new object. Instead of committing the object, and then deleting it, you can simply cancel the write transaction:
realm.beginWriteTransaction();
User user = realm.createObject(User.class);
// ...
realm.cancelTransaction();Please note that writes block each other, and will block the thread they are made on if other writes are in progress. Thanks to Realm’s MVCC architecture, reads are not blocked while a write transaction is open! This means that unless you need to make simultaneous writes from many threads at once, you should favor larger write transactions that do more work over many fine-grained write transactions. When you commit a write transaction to a Realm, all other instances of that Realm will be notified, and the read implicit transactions will refresh your Realm objects automatically.
Unless you need to make simultaneous writes from many threads at once, you should favor larger write transactions that do more work over many fine-grained write transactions.
The implicit read and write transactions implement the ACID properties of Realm.
Queries
All fetches (including queries) are lazy in Realm, and the data is never copied.
Realm’s query engine uses a Fluent interface to construct multi-clause queries.
To find all users named John or Peter you would write:
// Build the query looking at all users:
RealmQuery<User> query = realm.where(User.class);
// Add query conditions:
query.equalTo("name", "John");
query.or().equalTo("name", "Peter");
// Execute the query:
RealmResults<User> result1 = query.findAll();
// Or alternatively do the same all at once (the "Fluent interface"):
RealmResults<User> result2 = realm.where(User.class)
.equalTo("name", "John")
.or()
.equalTo("name", "Peter")
.findAll();This gives you a new RealmResults, of users with the name John or Peter. Objects are not copied - you get a list of references to the matching objects, and you work directly with the original objects that matches your query.
If you are going to modify or delete any of the objects in a RealmResults, you must do so in a write transaction. Otherwise, the implicit read is just fine, and you can access the objects without any delay.
Conditions
The following hopefully self explanatory conditions are supported:
between,greaterThan(),lessThan(),greaterThanOrEqualTo()&lessThanOrEqualTo()equalTo()¬EqualTo()contains(),beginsWith()&endsWith()
Not all conditions are applicable for all data types. Please consult the API reference for RealmQuery for details.
Logical Operators
Each condition is implicitly logical-and together. Logical-or must be applied explicitly with or().
You can also also group conditions with “parentheses” to specify order of evaluation: beginGroup() is your “left parenthesis” and endGroup() your “right parenthesis”:
RealmResults<User> r = realm.where(User.class)
.greaterThan("age", 10) //implicit AND
.beginGroup()
.equalTo("name", "Peter")
.or()
.contains("name", "Jo")
.endGroup()
.findAll();Sorting
Once you have done your query, you can sort the results like this:
RealmResults<User> result = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
RealmResults<User> sortedAscending = result.sort("age");
RealmResults<User> sortedDescending = result.sort("age", RealmResults.SORT_ORDER_DECENDING);Chaining Queries
Since results are never copied and computed on request, you can very efficiently chain queries to gradually filter your data:
RealmResults<Person> teenagers = realm.where(Person.class).between("age", 13, 20).findAll();
Person firstJohn = teenagers.where().equalTo("name", "John").findFirst();Aggregation
A RealmResults also has various aggregation methods:
RealmResults<User> results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
long sum = results.sum("age").longValue();
long min = results.min("age").longValue();
long max = results.max("age").longValue();
double average = results.average("age");
long matches = results.size();Iterations
To iterate through all objects in a RealmResults you can take advantage of Iterable:
RealmResults<User> results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
for (User u : results) {
// ... do something with the object ...
}or use a traditional for loop:
RealmResults<User> results = realm.where(User.class).findAll();
for (int i = 0; i < results.size(); i++) {
User u = results.get(i);
// ... do something with the object ...
}Deletion
You can delete the results of a query from the Realm:
// All changes to data must happen in a transaction
realm.beginTransaction();
// remove single match
result.remove(0);
result.removeLast();
// Delete all matches
result.clear();
realm.commitTransaction()Realms
Realms are our equivalent of a database: they contain different kinds of objects, and map to one file on disk.
The Default Realm
You may have noticed so far that we have always initialized access to our realm variable by calling Realm.getInstance(this). This singleton method will return an instance variable for your thread, that maps to a file called default.realm, located at the root of the File directory for your application.
Other Realms
It’s sometimes useful to have multiple realms, persisted at different locations, for example if you have different data groupings, different databases per feature, or you need to package some read-only files with your app, separate from the database your users will be editing.
Realm realm = Realm.getInstance(this, "allmymovies.realm");Using a Realm across Threads
The only rule to using Realm across threads is to remember that Realm, RealmObject or RealmResults instances cannot be passed across threads. When you want to access the same data from different threads, you should simply obtain a separate Realm instance for each thread (i.e. Realm.getInstance(this) or its cousins) and get your objects through a RealmQuery. The objects will map to the same data on disk, and will be readable & writeable from any thread!
Relationships
Any two RealmObjects can be linked together.
public class Email extends RealmObject {
private String address;
private boolean active;
// ... setters and getters left out
}
public class Contact extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private Email email;
// ... setters and getters left out
}Relationships are generally cheap in Realm. This means that following a link is not expensive in terms of speed, and the internal presentation of relationships is highly efficient in terms of memory consumption.
Many-to-One
Simply declare a property with the type of one of you RealmObject subclasses:
public class Contact extends RealmObject {
private Email email;
// Other fields…
}Each contact (instance of Contact) have either 0 or 1 email (instance of Email). In Realm, nothing prevent you from using the same email object in multiple contacts, and the model above can be a many-to-one relationship but often used to model one-to-one relationships.
Many-to-Many
You can establish a relationship to 0, 1 or more objects from a single object via an RealmList<T> field declaration
public class Contact extends RealmObject {
private RealmList<Email> emails;
// Other fields…
}RealmLists are basically containers of RealmObjects, that behave very much like a regular Java List. There is no limitation in Realm to using the same object twice (or more) in different RealmLists, and you can use this to model both one-to-many, and many-to-many relationsships.
You can add standard getters & setters to access the data in the link.
realm.beginTransaction();
Contact contact = realm.createObject(Contact.class);
contact.setName("John Doe");
Email email1 = realm.createObject(Email.class);
email1.setAddress("john@example.com");
email1.setActive(true);
contact.getEmails().add(email1);
Email email2 = realm.createObject(Email.class);
email2.setNumber("jd@example.com");
email2.setActive(false);
contact.getEmails().add(email2);
realm.commitTransaction();It is possible to declare recursive relationships which can be useful when modelling certain types of data.
public class Person extends RealmObject {
private String name;
private RealmLink<Person> friends;
// Other fields…
}Use recursive relationships with care as Realm does not currently have cycle detection and you can easily end in infinite loops.
Link queries
It is possible to query links or relationships. Consider the model above. If you wish to find all contacts with an active email address, you can do:
RealmResults<Contact> contacts = realm.where(Contact.class).equalTo("emails.active", true).findAll();First of all, notice that the field name in the equalsTo condition contains the path through the relationships (separated by period .).
The query above should be read “give me all contacts with at least one active email address”. It is important to understand that the result will contain the Email objects which do not fulfill the condition since they are part of the Contact objects.
Notifications
If you have a backgroud thread adding data to a Realm, your UI or other threads can get notified of changes in a realm by adding a listener, which is executed when the Realm is changed (by another thread or process):
realm.addChangeListener(new RealmChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onChange() {
// ... do something with the updates (UI, etc.) ...
}
});You can easily close all listeners when needed:
realm.removeAllChangeListeners();Migrations
When working with any database, it is likely your data model will change over time. Since data models in Realm are defined as standard Objects, changing them is as easy as changing the interface of the corresponding RealmObject subclass.
Just changing your code to the new definition will work fine, if you have no data stored on disk under the old schema. But if you do, there will be a mismatch between what Realm sees defined in code, and the data Realm sees on disk, and an exception will be thrown.
We provide built-in methods so you can upgrade your schema on disk, and the data you stored for previous versions of the schema. See our migrationSample app for details.
Encryption
Please take note of the Export Compliance section of our LICENSE, as it places restrictions against the usage of Realm if you are located in countries with an export restriction or embargo from the United States.
The Realm file can be stored encrypted on disk by passing a 256-bit encryption key to Realm.create():
byte[] key = new byte[32];
new SecureRandom().nextBytes(key);
Realm realm = Realm.create(this, key);
// ... use the Realm as normal ...This ensures that all data persisted to disk is transparently encrypted and decrypted with standard AES-256 encryption. The same encryption key must be supplied each time a Realm instance for the file is created.
See examples/encryptionExample for a complete example of how to securely store keys between runs in the Android KeyStore so that other applications cannot read them.
Using Encryption requires building Realm from source.
- Follow the normal build instructions, but before running
./gradlew assemble, add the lineencryption=truetolocal.properties. - After building Realm, replace the copy of
realm-<VERSION>.aarin your project with the one found atrealm/build/outputs/aar/realm-<VERSION>.aar.
Next Steps
You can look at our examples to see Realm used in practice in an app. (We’re getting more samples ready!)
Happy hacking! You can always talk to a live human developer on realm-java.
FAQ
Should I use Realm in production applications?
Realm has been used in production in commercial products since 2012.
You should expect our Java APIs to break as we evolve the product from community feedback — and you should expect more features & bugfixes to come along as well.
Do I have to pay to use Realm?
No, Realm for Android is entirely free to use, even in commercial projects.
How do you all plan on making money?
We’re actually already generating revenue selling enterprise products and services around our technology. If you need more than what is currently in our releases or in realm-java, we’re always happy to chat by email. Otherwise, we are committed to developing realm-java in the open, and to keep it free and open-source under the Apache 2.0 license.
I see references to “tightdb” or a “core” in the code, what is that?
TightDB is the old name of our core C++ storage engine. The core is not currently open-source but we do plan on open-sourcing it, also under the Apache 2.0 license, once we’ve had a chance to clean it, rename it and finalize our synchronization implementation inside of it. In the meantime, its binary releases are made available under the Realm Core (TightDB) Binary License.