This is not the current version. View the latest documentation
If you’re looking to use Realm from Objective‑C, or from mixed Objective‑C & Swift apps please see Realm Objective‑C instead. Using both Realm Objective‑C and Realm Swift simultaneously is not supported.
Realm Swift enables you to efficiently write your app’s model layer in a safe, persisted and fast way. Here’s what it looks like:
// Define your models like regular Swift classes
class Dog: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
dynamic var age = 0
}
class Person: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
dynamic var picture: NSData? = nil // optionals supported
let dogs = List<Dog>()
}
// Use them like regular Swift objects
let mydog = Dog()
mydog.name = "Rex"
print("name of dog: \(mydog.name)")
// Persist your data easily
let realm = try! Realm()
try! realm.write {
realm.add(mydog)
}
// Query it from any thread
dispatch_async(dispatch_queue_create("background", nil)) {
realm.objects(Dog).filter("age > 8") // => Results<Dog>
}If you have an app that is presently using Core Data and have been considering switching to Realm, we recently published an article discussing how to go about doing this. Go check it out!
Getting Started
Download Realm Swift or see the source on GitHub.
Prerequisites
- Apps using Realm can target: iOS 8 or later, OS X 10.9 or later & WatchKit. (iOS 7 cannot be supported because it does not allow using 3rd party dynamic frameworks, and it is impossible to build static libraries that contain Swift code.)
- Xcode 6.4 or later required.
- Current releases of Realm Swift target Swift 2.1. Using Swift 2.0 and Swift 1.2 is possible, but support has to be enabled manually. We will deprecate our Swift 1.2 support at some point in the coming months.
Installation (Swift 2.1)
- Download the latest release of Realm and extract the zip.
- Go to your Xcode project’s “General” settings. Drag
RealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theios/swift-2.1,watchos/orosx/swift-2.1directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section. Make sure Copy items if needed is selected and click Finish. - In your unit test target’s “Build Settings”, add the parent path to
RealmSwift.frameworkin the “Framework Search Paths” section. - If using Realm in an iOS or watchOS project, create a new “Run Script Phase” in your app’s target’s “Build Phases” and paste the following snippet in the script text field:
bash "${BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR}/${FRAMEWORKS_FOLDER_PATH}/Realm.framework/strip-frameworks.sh"This step is required to work around an App Store submission bug when archiving universal binaries.
- Install CocoaPods 0.39.0 or later.
- In your Podfile, add
use_frameworks!andpod 'RealmSwift'to your main and test targets. - From the command line, run
pod install. - Use the
.xcworkspacefile generated by CocoaPods to work on your project!
- Install Carthage 0.9.2 or later.
- Add
github "realm/realm-cocoa"to your Cartfile. - Run
carthage update. - iOS: Drag
RealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theCarthage/Build/iOS/directory to the “Linked Frameworks and Libraries” section of your Xcode project’s “General” settings.
OS X: DragRealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theCarthage/Build/Mac/directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section of your Xcode project’s “General” settings.
watchOS: DragRealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theCarthage/Build/watchOS/directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section of your Xcode project’s “General” settings. -
iOS: On your application targets’ “Build Phases” settings tab, click the “+” icon and choose “New Run Script Phase”. Create a Run Script with the following contents:
/usr/local/bin/carthage copy-frameworksand add the paths to the frameworks you want to use under “Input Files”, e.g.:
$(SRCROOT)/Carthage/Build/iOS/Realm.framework
$(SRCROOT)/Carthage/Build/iOS/RealmSwift.frameworkThis script works around an App Store submission bug triggered by universal binaries.
Installation (Swift 2.0)
Swift 2.0 support is available when building Realm from source. Our prepackaged releases only support Swift 1.2 & Swift 2.1.
- Clone Realm from our repository on GitHub.
- Run
git checkout 0.96.3in the cloned repository to check out the release tag. - Run
REALM_SWIFT_VERSION=2.0 sh build.sh buildin the cloned repository to build the frameworks. - Make sure that you remove the existing binaries of
RealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom your project. - Go to your Xcode project’s “General” settings. Drag the versions of
RealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrombuild/ios/swift-2.0/orbuild/osx/swift-2.0/directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section. Make sure Copy items if needed is selected and click Finish. - In your unit test target’s “Build Settings”, add the parent path to
RealmSwift.frameworkin the “Framework Search Paths” section.
- Install CocoaPods 0.39.0 or later.
- In your Podfile, add
use_frameworks!andpod 'RealmSwift'to your main and test targets. - From the command line, run
pod install. - Use the
.xcworkspacefile generated by CocoaPods to work on your project!
Installation (Swift 1.2)
We’ll still be supporting Swift 1.2 via the swift-1.2 branch for some time to come, but we encourage you to move to Swift 2 as soon as possible.
- Download the latest release of Realm and extract the zip.
- Go to your Xcode project’s “General” settings. Drag
RealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theios/swift-1.2orosx/swift-1.2directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section. Make sure Copy items if needed is selected and click Finish. - In your unit test target’s “Build Settings”, add the parent path to
RealmSwift.frameworkin the “Framework Search Paths” section. - If using Realm in an iOS or watchOS project, create a new “Run Script Phase” in your app’s target’s “Build Phases” and paste the following snippet in the script text field:
bash "${BUILT_PRODUCTS_DIR}/${FRAMEWORKS_FOLDER_PATH}/Realm.framework/strip-frameworks.sh"This step is required to work around an App Store submission bug when archiving universal binaries.
In your Podfile, add the following to your main and test targets:
# You need to add both “Realm” & “RealmSwift”
use_frameworks!
pod 'Realm', :git => 'https://github.com/realm/realm-cocoa.git', :branch => 'swift-1.2'
pod 'RealmSwift', :git => 'https://github.com/realm/realm-cocoa.git', :branch => 'swift-1.2'N.B.: The last Swift 1.2 release of Realm Swift available via Carthage is 0.95.0.
- Install Carthage 0.9.2 or later.
- Add
github "realm/realm-cocoa"to your Cartfile. - Run
carthage update. - iOS: Drag
RealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theCarthage/Build/iOS/directory to the “Linked Frameworks and Libraries” section of your Xcode project’s “General” settings.
OS X: DragRealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theCarthage/Build/Mac/directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section of your Xcode project’s “General” settings.
watchOS: DragRealmSwift.frameworkandRealm.frameworkfrom theCarthage/Build/watchOS/directory to the “Embedded Binaries” section of your Xcode project’s “General” settings. -
iOS: On your application targets’ “Build Phases” settings tab, click the “+” icon and choose “New Run Script Phase”. Create a Run Script with the following contents:
/usr/local/bin/carthage copy-frameworksand add the paths to the frameworks you want to use under “Input Files”, e.g.:
$(SRCROOT)/Carthage/Build/iOS/Realm.framework
$(SRCROOT)/Carthage/Build/iOS/RealmSwift.frameworkThis script works around an App Store submission bug triggered by universal binaries.
tvOS
Although tvOS is in beta, we’re currently evaluating what Realm would look like on the platform. If you’d like to evaluate early builds of Realm for tvOS, for development purposes only, not suitable for production, see PR #2506 for details.
Realm Browser
If you’ve already updated to Realm Swift 0.96 or later, there is a compatible release of the Browser on the Realm Browser GitHub page.
We also provide a standalone Mac app named Realm Browser to read and edit .realm databases.
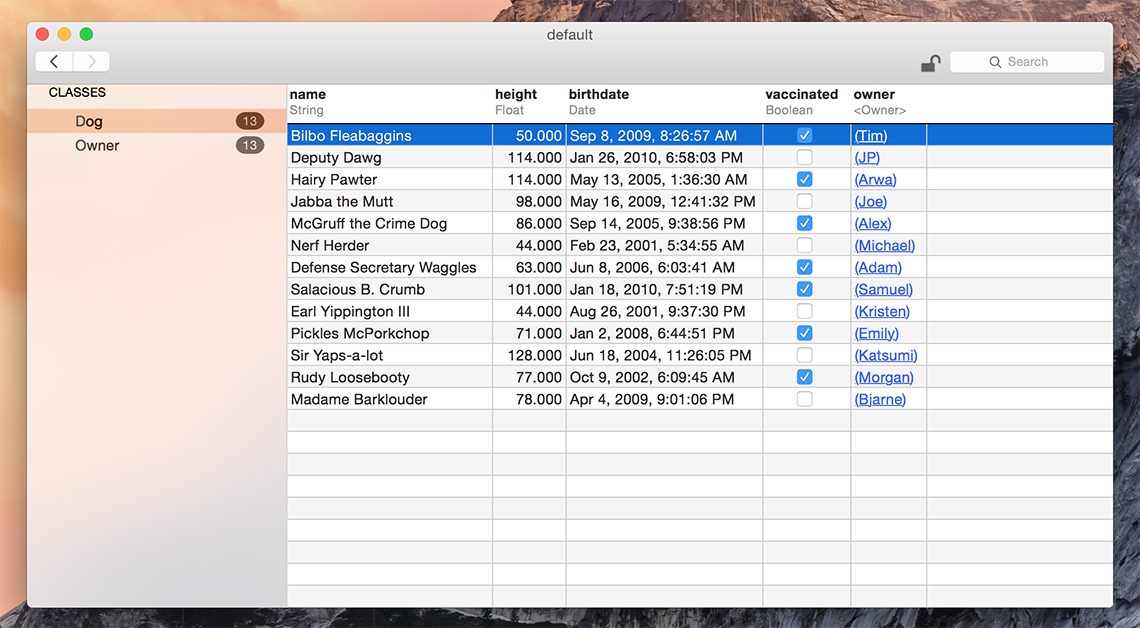
You can generate a test database with sample data using the menu item Tools > Generate demo database.
If you need help finding your app’s Realm file, check this StackOverflow answer for detailed instructions.
The Realm Browser is available on the Mac App Store.
Xcode Plugin
Our Xcode plugin makes it easy to generate new Realm models.
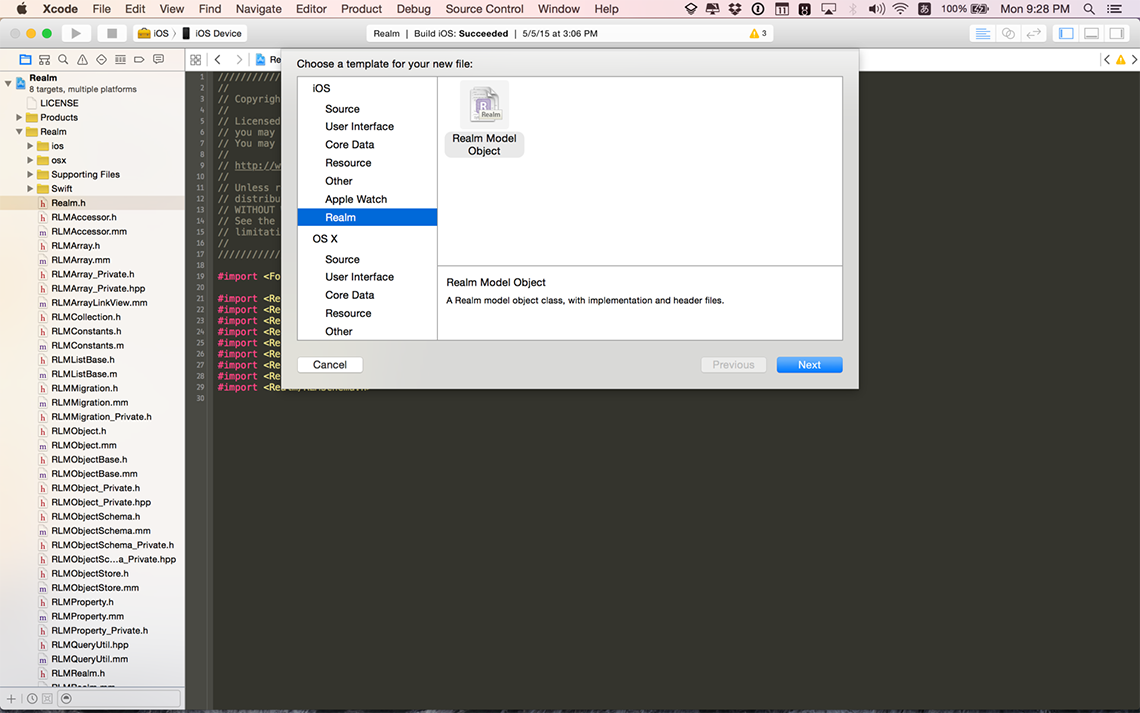
The easiest way to install the Realm Xcode plugin is through Alcatraz under the name “RealmPlugin”. You can also install the plugin manually by opening plugin/RealmPlugin.xcodeproj contained in the release zip and clicking build. You will need to quit and relaunch Xcode to see our plugin. If you use the Xcode menu to create a new file (File > New > File… — or ⌘N) you should see a new option to create a new Realm model.
API Reference
You can consult our full API reference for all classes, methods & more.
Examples
You can find example applications for both iOS and OS X in our release zip under examples/, demonstrating how to use many features of Realm like migrations, how to use it with UITableViewControllers, encryption, command-line tools and much more.
Getting Help
- Need help with your code? Ask on StackOverflow. We actively monitor & answer questions on SO!
- Have a bug to report? Open an issue on our repo. If possible, include the version of Realm, a full log, the Realm file, and a project that shows the issue.
- Have a feature request? Open an issue on our repo. Tell us what the feature should do, and why you want the feature.
If you’re using a crash reporter (like Crashlytics or HockeyApp), make sure to enable log collection. Realm logs metadata information (but no user data) when throwing exceptions and in irrecoverable situations, and these messages can help debug when things go wrong.
Models
Realm data models are defined using regular Swift classes with properties. Simply subclass Object or an existing model class to create your Realm data model objects. Realm model objects mostly function like any other Swift objects - you can add your own methods and protocols to them and use them like you would any other object. The main restriction is that you can only use an object on the thread which it was created.
If you have installed our Xcode Plugin there will be a nice template to create the Swift file in the “New File…” dialog.
Relationships and nested data structures are modeled simply by including properties of the target type or Lists for typed lists of objects.
import RealmSwift
// Dog model
class Dog: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
dynamic var owner: Person? // Properties can be optional
}
// Person model
class Person: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
dynamic var birthdate = NSDate(timeIntervalSince1970: 1)
let dogs = List<Dog>()
}Since Realm parses all models defined in your code at launch, they must all be valid, even if they are never used.
When using Realm from Swift, the Swift.reflect(_:) function is used to determine information about your models, which requires that calling init() succeed. This means that all non-optional properties must have a default value.
See Object for more details.
Supported Types
Realm supports the following property types: Bool, Int8, Int16, Int32, Int64, Double, Float, String, NSDate truncated to the second, and NSData.
CGFloat properties are discouraged, as the type is not platform independent.
String, NSDate and NSData properties can be optional. Object properties must be optional. Storing optional numbers is done using RealmOptional.
Relationships
Objects can be linked to each other by using Object and List properties. Lists have an interface very similar to Array and objects contained in a List can be accessed using indexed subscripting. Unlike Arrays, Lists only hold Objects of a single subclass type. For more details see List.
Assuming your Person model has already been defined (see above) let’s create another model called Dog:
class Dog: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
}
To-One Relationships
For many-to-one or one-to-one relationships, simply declare a property with the type of your Object subclass:
class Dog: Object {
// ... other property declarations
dynamic var owner: Person? // to-one relationships must be optional
}You can use this property like you would any other:
let jim = Person()
let rex = Dog()
rex.owner = jimWhen using Object properties, you can access nested properties using normal property syntax. For example rex.owner?.address.country will traverse the object graph and automatically fetch each object from Realm as needed.
To-Many Relationships
You can define a to-many relationship using List properties. Lists contain other Objects of a single type and have an interface very similar to a mutable Array.
To add a “dogs” property on our Person model that links to multiple dogs, we can declare a property of type List<Dog>:
class Person: Object {
// ... other property declarations
let dogs = List<Dog>()
}You can access and assign List properties as usual:
let someDogs = realm.objects(Dog).filter("name contains 'Fido'")
jim.dogs.appendContentsOf(someDogs)
jim.dogs.append(rex)Inverse Relationships
Links are unidirectional. So if a to-many property Person.dogs links to a Dog instance and a to-one property Dog.owner links to Person, these links are independent from one another. Appending a Dog to a Person instance’s dogs property, doesn’t automatically set the dog’s owner property to this Person. Because manually synchronizing pairs of relationships is error prone, complex and duplicates information, Realm exposes an API to retrieve backlinks described below.
With inverse relationships, you can obtain all objects linking to a given object through a specific property. For example, calling Object().linkingObjects(_:forProperty:) on a Dog instance will return all objects of the specified class linking to the calling instance with the specified property. It’s possible to simplify this pattern by defining a read-only (computed) owners property on Dog:
class Dog: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
dynamic var age = 0
var owners: [Person] {
// Realm doesn't persist this property because it only has a getter defined
// Define "owners" as the inverse relationship to Person.dogs
return linkingObjects(Person.self, forProperty: "dogs")
}
}Optional Properties
String, NSDate, and NSData properties can be declared as optional or non-optional using the standard Swift syntax. Optional numeric types are declared using RealmOptional:
class Person: Object {
// Optional string property, defaulting to nil
dynamic var name: String? = nil
// Optional int property, defaulting to nil
// RealmOptional properties should always be declared with `let`,
// as assigning to them directly will not work as desired
let age = RealmOptional<Int>()
}
let realm = try! Realm()
try! realm.write() {
var person = realm.create(Person.self, value: ["Jane", 27])
// Reading from or modifying a `RealmOptional` is done via the `value` property
person.age.value = 28
}RealmOptional supports Int, Float, Double, Bool, and all of the sized versions of Int (Int8, Int16, Int32, Int64).
Property Attributes
Realm model properties need the dynamic var attribute in order for these properties to become accessors for the underlying database data.
There are two exceptions to this: List and RealmOptional properties cannot be declared as dynamic because generic properties cannot be represented in the Objective‑C runtime, which is used for dynamic dispatch of dynamic properties, and should always be declared with let.
Indexed Properties
Override Object.indexedProperties() to set which properties in your model should be indexed:
class Book: Object {
dynamic var price = 0
dynamic var title = ""
override static func indexedProperties() -> [String] {
return ["title"]
}
}Currently only strings and integers can be indexed.
Indexing a property will greatly speed up queries where the property is compared for equality (i.e. the = and IN operators), at the cost of slower insertions.
Primary Keys
Override Object.primaryKey() to set the model’s primary key. Declaring a primary key allows objects to be looked up and updated efficiently and enforces uniqueness for each value. Once an object with a primary key is added to a Realm, the primary key cannot be changed.
class Person: Object {
dynamic var id = 0
dynamic var name = ""
override static func primaryKey() -> String? {
return "id"
}
}Ignored Properties
Override Object.ignoredProperties() to prevent Realm from persisting model properties. Realm won’t interfere with the regular operation of these properties: they’ll be backed by ivars and you can freely override their setters and getters.
class Person: Object {
dynamic var tmpID = 0
var name: String { // read-only properties are automatically ignored
return "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
dynamic var firstName = ""
dynamic var lastName = ""
override static func ignoredProperties() -> [String] {
return ["tmpID"]
}
}Writes
All changes to an object (addition, modification and deletion) must be done within a write transaction.
Realm objects can be instantiated and used as ‘standalone’ objects (i.e. not stored in a Realm) just like regular Swift objects. To share objects between threads or re-use them between app launches you must persist them to a Realm, an operation which must be done within a write transaction.
Since write transactions incur non-negligible overhead, you should architect your code to minimize the number of write transactions.
Because write transactions could potentially fail like any other disk IO operations, both Realm.write() & Realm.commitWrite() are marked as throws so you can handle and recover from failures like running out of disk space. There are no other recoverable errors. For brevity, our code samples don’t handle these errors but you certainly should in your production applications.
Creating Objects
When you have defined a model you can instantiate your Object subclass and add the new instance to the Realm. Consider this simple model:
class Dog: Object {
dynamic var name = ""
dynamic var age = 0
}We can create new objects in several ways:
// (1) Create a Dog object and then set its properties
var myDog = Dog()
myDog.name = "Rex"
myDog.age = 10
// (2) Create a Dog object from a dictionary
let myOtherDog = Dog(value: ["name" : "Pluto", "age": 3])
// (3) Create a Dog object from an array
let myThirdDog = Dog(value: ["Fido", 5])- The most obvious is to use the designated initializer to create an object.
- Objects can also be created from dictionaries using appropriate keys and values.
- Finally, Object subclasses can be instantiated using arrays. The values in the array have to be in the same order as the corresponding properties in the model.
Nested Objects
If an object has properties that are Objects or Lists, these can be set recursively using nested arrays and/or dictionaries. You simply replace each object with a dictionary or array representing its properties:
// Instead of using already existing dogs...
let aPerson = Person(value: ["Jane", 30, [aDog, anotherDog]])
// ...we can create them inline
let anotherPerson = Person(value: ["Jane", 30, [["Buster", 5], ["Buddy", 6]]])This will work for any combination of nested arrays and dictionaries. Note that a List may only contain Objects, not basic types such as String.
Adding Objects
You can add an object to a Realm like so:
// Create a Person object
let author = Person()
author.name = "David Foster Wallace"
// Get the default Realm
let realm = try! Realm()
// You only need to do this once (per thread)
// Add to the Realm inside a transaction
try! realm.write {
realm.add(author)
}After you have added the object to the Realm you can continue using it, and all changes you make to it will be persisted (and must be made within a write transaction). Any changes are made available to other threads that use the same Realm when the write transaction is committed.
Please note that writes block each other, and will block the thread they are made on if multiple writes are in progress. This is similar to other persistence solutions and we recommend that you use the usual best-practices for this situation, namely offloading your writes to a separate thread.
Due to Realm’s MVCC architecture, reads are not blocked while a write transaction is open. Unless you need to make simultaneous writes from many threads at once, you should favor larger write transactions that do more work over many fine-grained write transactions.
See Realm and Object for more details.
Updating Objects
Realm provides a few ways to update objects, all of which offer different tradeoffs depending on the situation. Choose which one is best for your situation:
Typed Updates
You can update any object by setting its properties within a write transaction.
// Update an object with a transaction
try! realm.write {
author.name = "Thomas Pynchon"
}Updating Objects With Primary Keys
If you have a primary key on your model, you can update an object or insert a new one if it doesn’t exist yet using Realm().add(_:update:).
// Creating a book with the same primary key as a previously saved book
let cheeseBook = Book()
cheeseBook.title = "Cheese recipes"
cheeseBook.price = 9000
cheeseBook.id = 1
// Updating book with id = 1
try! realm.write {
realm.add(cheeseBook, update: true)
}If a book with a primary key id of 1 was not in the database, this would create a new book instead.
You can also partially update objects with primary keys by passing the subset of values you wish to update, along with the primary key:
// Assuming a "Book" with a primary key of `1` already exists.
try! realm.write {
realm.create(Book.self, value: ["id": 1, "price": 9000.0], update: true)
// the book's `title` property will remain unchanged.
}Key-Value Coding
Object, Result, and List all conform to key-value coding (KVC). This can be useful when you need to determine which property to update at runtime.
Applying KVC to a collection is a great way to update objects in bulk without the overhead of iterating over a collection while creating accessors for every item.
let persons = realm.objects(Person)
try! realm.write {
persons.first?.setValue(true, forKeyPath: "isFirst")
// set each person's planet property to "Earth"
persons.setValue("Earth", forKeyPath: "planet")
}Deleting Objects
Pass the object to be deleted to the Realm().delete(_:) method within a write transaction.
// let cheeseBook = ... Book stored in Realm
// Delete an object with a transaction
try! realm.write {
realm.delete(cheeseBook)
}You can also delete all objects stored in a Realm. Note the Realm file will maintain its size on disk to efficiently reuse that space for future objects.
// Delete all objects from the realm
try! realm.write {
realm.deleteAll()
}Queries
Queries return a Results instance, which contains a collection of Objects. Results have an interface very similar to Array and objects contained in a Results can be accessed using indexed subscripting. Unlike Arrays, Results only hold Objects of a single subclass type.
All queries (including queries and property access) are lazy in Realm. Data is only read when the properties are accessed.
Results to a query are not copies of your data: modifying the results of a query (within a write transaction) will modify the data on disk directly. Similarly, you can traverse your graph of relationships directly from the Objects contained in a Results.
The most basic method for retrieving objects from a Realm is Realm().objects(_:), which returns a Results of all Object instances of the subclass type being queried the default Realm.
let dogs = realm.objects(Dog) // retrieves all Dogs from the default Realm
Filtering
If you’re familiar with NSPredicate, then you already know how to query in Realm. Objects, Realm, List, and Results all provide methods that allow you to query for specific Object instances by simply passing in an NSPredicate instance, predicate string, or predicate format string just as you would when querying an NSArray.
For example, the following would extend our earlier example by calling Results().filter(_:...) to retrieve all dogs with the color tan and names beginning with ‘B’ from the default Realm:
// Query using a predicate string
var tanDogs = realm.objects(Dog).filter("color = 'tan' AND name BEGINSWITH 'B'")
// Query using an NSPredicate
let predicate = NSPredicate(format: "color = %@ AND name BEGINSWITH %@", "tan", "B")
tanDogs = realm.objects(Dog).filter(predicate)See Apple’s Predicates Programming Guide for more information about building predicates and use our NSPredicate Cheatsheet. Realm supports many common predicates:
- The comparison operands can be property names or constants. At least one of the operands must be a property name.
- The comparison operators ==, <=, <, >=, >, !=, and BETWEEN are supported for Int, Int8, Int16, Int32, Int64, Float, Double and NSDate property types. Such as age == 45
- Identity comparisons ==, !=, e.g.
Results<Employee>().filter("company == %@", company) - The comparison operators == and != are supported for boolean properties.
- For String and NSData properties, we support the ==, !=, BEGINSWITH, CONTAINS, and ENDSWITH operators, such as name CONTAINS ‘Ja’
- Case insensitive comparisons for strings, such as name CONTAINS[c] ‘Ja’. Note that only characters “A-Z” and “a-z” will be ignored for case.
- Realm supports the following compound operators: “AND”, “OR”, and “NOT”. Such as name BEGINSWITH ‘J’ AND age >= 32
- The containment operand IN such as name IN {‘Lisa’, ‘Spike’, ‘Hachi’}
- Nil comparisons ==, !=, e.g.
Results<Company>().filter("ceo == nil"). Note that Realm treatsnilas a special value rather than the absence of a value, so unlike with SQLnilequals itself. - ANY comparisons, such as ANY student.age < 21
- The aggregate expressions
@count,@min,@max,@sumand@avgare supported on List properties, e.g.realm.objects(Company).filter("employees.@count > 5")to find all companies with more than five employees.
For more, see Results().filter(_:...).
Sorting
Results allows you to specify a sort criteria and order based on a single or multiple properties. For example, the following calls sorts the returned dogs from the example above alphabetically by name:
// Sort tan dogs with names starting with "B" by name
let sortedDogs = realm.objects(Dog).filter("color = 'tan' AND name BEGINSWITH 'B'").sorted("name")For more, see Results().sorted(_:) and Results().sorted(_:ascending:).
Chaining
One unique property of Realm’s query engine is the ability to chain queries with very little transactional overhead when compared to traditional databases that require a separate trip to the database server for each successive query.
For example, if we wanted a result set for just the tan colored dogs, and the tan colored dogs whose names also started with ‘B’, you might chain two queries like this:
let tanDogs = realm.objects(Dog).filter("color = 'tan'")
let tanDogsWithBNames = tanDogs.filter("name BEGINSWITH 'B'")Auto-Updating
Results are live, auto-updating views into the underlying data, which means results never have to be re-fetched. Modifying objects that affect the query will be reflected in the results immediately.
let puppies = realm.objects(Dog).filter("age < 2")
puppies.count // => 0
try! realm.write {
realm.create(Dog.self, value: ["name": "Fido", "age": 1])
}
puppies.count // => 1This applies to all Results: all objects, filtered & chained.
This property of Results not only keeps Realm fast and efficient, it allows your code to be simpler and more reactive. For example, if your view controller relies on the results of a query, you can store the Results in a property and access it without having to make sure to refresh its data prior to each access.
You can subscribe to Realm notifications to know when Realm data is updated, indicating when your app’s UI should be refreshed for example, without having to re-fetch your Results.
Since results are auto-updating, it’s important to not rely on indices & counts staying constant. The only time a Results is frozen is when fast-enumerating over it, which makes it possible to mutate the objects matching a query while enumerating over it:
try! realm.write {
for person in realm.objects(Person).filter("age == 10") {
person.age++
}
}Alternatively, use key-value coding to perform operations on Results.
Realms
The Default Realm
You may have noticed so far that we have initialized access to our realm variable by calling Realm(). That method returns a Realm object that maps to a file called “default.realm” under the Documents folder (iOS) or Application Support folder (OS X) of your app.
Realm Configuration
Configuring things like where your Realm files are stored is done through Realm.Configuration. The configuration can either be passed to Realm(configuration: config) each time you need a Realm instance, or you can set the configuration to use for the default Realm with Realm.Configuration.defaultConfiguration = config.
For example, suppose you have an application where users have to log in to your web backend, and you want to support quickly switching between accounts. You could give each account its own Realm file that will be used as the default Realm by doing the following:
func setDefaultRealmForUser(username: String) {
var config = Realm.Configuration()
// Use the default directory, but replace the filename with the username
config.path = NSURL.fileURLWithPath(config.path!)
.URLByDeletingLastPathComponent?
.URLByAppendingPathComponent("\(username).realm")
.path
// Set this as the configuration used for the default Realm
Realm.Configuration.defaultConfiguration = config
}Other Realms
It’s sometimes useful to have multiple Realms persisted at different locations. For example, you may want to bundle some data with your application in a Realm file, in addition to your main Realm. You can do this with the following code:
let config = Realm.Configuration(
// Get the path to the bundled file
path: NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource("MyBundledData", ofType:"realm"),
// Open the file in read-only mode as application bundles are not writeable
readOnly: true)
// Open the Realm with the configuration
let realm = try! Realm(configuration: config)
// Read some data from the bundled Realm
let results = realm.objects(Dog).filter("age > 5")Please note that if a custom path is used to initialize a Realm, it must be in a location with write permissions. The most common location to store writable Realm files is the “Documents” directory on iOS and the “Application Support” directory on OS X. Please respect Apple’s iOS Data Storage Guidelines, which recommend that documents that can be regenerated be stored in the <Application_Home>/Library/Caches directory.
In-Memory Realms
Normally Realms are persisted to disk, but you can also create ones which operate purely in memory by setting the inMemoryIdentifier rather than the path on your Realm.Configuration.
let realm = try! Realm(configuration: Realm.Configuration(inMemoryIdentifier: "MyInMemoryRealm"))In-memory Realms do not save data across app launches, but all other features of Realm will work as expected, including querying, relationships and thread-safety. This is a useful option if you need flexible data access without the overhead of disk persistence.
In-memory Realms create several files in a temporary directory for coordinating things like cross-process notifications. No data is actually written to the files unless the operating system needs to swap to disk due to memory pressure.
Notice: When all in-memory Realm instances with a particular identifier go out of scope with no references, all data is freed for that Realm. It is recommended that you hold onto a strong reference to any created in-memory Realms for the duration of your app.
Error Handling
Like any disk IO operation, creating a Realm instance could sometimes fail if resources are constrained. In practice, this can only happen the first time a Realm instance is created on a given thread. Subsequent accesses to a Realm from the same thread will reuse a cached instance and will always succeed.
To handle errors when first accessing a Realm on a given thread, use Swift’s built-in error handling mechanism:
do {
let realm = try Realm()
} catch let error as NSError {
// handle error
}Copying Objects Between Realms
Copying Realm objects to other Realms is as simple as passing in the original object to Realm().create(_:value:update:). For example, realm.create(MyObjectSubclass.self, value: originalObjectInstance). Remember that Realm objects can only be accessed from the thread on which they were first created, so this copy will only work for Realms on the same thread.
Finding a Realm File
If you need help finding your app’s Realm file, check this StackOverflow answer for detailed instructions.
Bundling a Realm with an App
It’s common to seed an app with initial data, making it available to your users immediately on first launch. Here’s how to do this:
- First, populate the realm. You should use the same data model as your final, shipping app to create a realm and populate it with the data you wish to bundle with your app. Since realm files are cross-platform, you can use an OS X app (see our JSONImport example) or your iOS app running in the simulator.
- In the code where you’re generating this realm file, you should finish by making a compacted copy of the file (see
Realm().writeCopyToPath(_:encryptionKey:)). This will reduce the Realm’s file size, making your final app lighter to download for your users. - Drag the new compacted copy of your realm file to your final app’s Xcode Project Navigator.
- Go to your app target’s build phases tab in Xcode and add the realm file to the “Copy Bundle Resources” build phase.
- At this point, your bundled realm file will be accessible to your app. You can find its path by using
NSBundle.mainBundle().pathForResource(_:ofType:). - If the bundled Realm contains fixed data that you don’t need to modify, you can open it directly from the bundle path by setting
readOnly = trueon the Realm.Configuration object. Otherwise, if it’s initial data that you’ll be modifying, you can copy the bundled file to your application’s Documents directory usingNSFileManager.defaultManager().copyItemAtPath(_:toPath:).
You can refer to our migration sample app for an example of how to use a bundled realm file.
Class Subsets
In some scenarios you may wish to limit which classes can be stored in a specific Realm. For example, if you have two teams working on different components of your application which both use Realm internally, you may not want to have to coordinate migrations between them. You can do this by setting the objectTypes property of your Realm.Configuration:
let config = Realm.Configuration(objectTypes: [MyClass.self, MyOtherClass.self])
let realm = try! Realm(configuration: config)
Threading
Within individual threads you can just treat everything as regular objects without worrying about concurrency or multithreading. There is no need for any locks or resource coordination to access them (even if they are simultaneously being modified on other threads) and it is only modifying operations that have to be wrapped in write transactions.
Realm makes concurrent usage easy by ensuring that each thread always has a consistent view of the Realm. You can have any number of threads working on the same Realms in parallel, and since they all have their own snapshots, they will never cause each other to see inconsistent state.
The only thing you have to be aware of is that you cannot have multiple threads sharing the same instances of Realm objects. If multiple threads need to access the same objects they will each need to get their own instances (otherwise changes happening on one thread could cause other threads to see incomplete or inconsistent data).
Seeing Changes From Other Threads
On the main UI thread (or any thread with a runloop) objects will automatically update with changes from other threads between each iteration of the runloop. At any other time you will be working on the snapshot, so individual methods always see a consistent view and never have to worry about what happens on other threads.
When you initially open a Realm, its state will be based off the most recent successful write commit, and it will remain on that version until refreshed. Realms are automatically refreshed at the start of every runloop iteration, unless Realm’s autorefresh property is set to NO. If a thread has no runloop (which is generally the case in a background thread), then Realm.refresh() must be called manually in order to advance the transaction to the most recent state.
Realms are also refreshed when write transactions are committed (Realm.commitWrite()).
Failing to refresh Realms on a regular basis could lead to some transaction versions becoming “pinned”, preventing Realm from reusing the disk space used by that version, leading to larger file sizes. Refer to our Current Limitations for more details on this effect.
Passing Instances Across Threads
Standalone (unpersisted) instances of Objects behave exactly as regular NSObject subclasses, and are safe to pass across threads.
Persisted instances of Realm, Object, Results, or List can only be used on the thread on which they were created, otherwise an exception is thrown*. This is one way Realm enforces transaction version isolation. Otherwise, it would be impossible to determine what should be done when an object is passed between threads at different transaction versions, with a potentially extensive relationship graph.
Instead, there are several ways to represent instances in ways that can be safely passed between threads. For example, an object with a primary key can be represented by its primary key’s value; or a Results can be represented by its NSPredicate or query string; or a Realm can be represented by its Realm.Configuration. The target thread can then re-fetch the Realm, Object, Results, or List using its thread-safe representation. Keep in mind that re-fetching will retrieve an instance at the version of the target thread, which may differ from the originating thread.
* Some properties and methods on these types can be accessed from any thread:
- Realm: all properties, class methods, and initializers.
- Object:
invalidated,objectSchema,realm, class methods, and initializers. - Results:
objectClassNameandrealm. - List:
invalidated,objectClassName, andrealm.
Using a Realm Across Threads
To access the same Realm file from different threads, you must initialize a new Realm to get a different instance for every thread of your app. As long as you specify the same configuration, all Realm instances will map to the same file on disk.
Sharing Realm instances across threads is not supported.
Realm instances accessing the same realm file must also all use the same Realm.Configuration.
Realm can be very efficient when writing large amounts of data by batching together multiple writes within a single transaction. Transactions can also be performed in the background using Grand Central Dispatch to avoid blocking the main thread. Realm objects are not thread safe and cannot be shared across threads, so you must get a Realm instance in each thread/dispatch_queue in which you want to read or write. Here’s an example of inserting a million objects in a background queue:
dispatch_async(queue) {
autoreleasepool {
// Get realm and table instances for this thread
let realm = try! Realm()
// Break up the writing blocks into smaller portions
// by starting a new transaction
for idx1 in 0..<1000 {
realm.beginWrite()
// Add row via dictionary. Property order is ignored.
for idx2 in 0..<1000 {
realm.create(Person.self, value: [
"name": "\(idx1)",
"birthdate": NSDate(timeIntervalSince1970: NSTimeInterval(idx2))
])
}
// Commit the write transaction
// to make this data available to other threads
try! realm.commitWrite()
}
}
}Notifications
Realm instances send out notifications to other instances on other threads every time a write transaction is committed. These notifications can be observed by registering a block:
// Observe Realm Notifications
let token = realm.addNotificationBlock { notification, realm in
viewController.updateUI()
}The notification stays active as long as a reference is held to the returned notification token. You should hold onto a strong reference to this token on the class registering for updates, as notifications are automatically un-registered when the notification token is deallocated.
See Realm().addNotificationBlock(_:) and Realm().removeNotification(_:) for details.
Key-Value Observation
Realm objects are Key-Value Observing compliant for most properties. All persisted (non-ignored) properties on your Object subclasses are KVO-compliant, along with the invalidated property on Object and List.
Observing properties of standalone instances of Object subclasses works just like with any other dynamic property, but note that you cannot add an object to a Realm (with realm.add(obj) or other similar methods) while it has any registered observers.
Observing properties of persisted objects works a little differently. With persisted objects, there are three times when the value of a property may change: when you directly assign to it; when you call realm.refresh() or the Realm is automatically refreshed after a write transaction is committed on a different thread; and when you call realm.beginWrite() after changes on a different thread which have not been picked up by a refresh on the current thread.
In the latter two cases, all of the changes made in the write transaction(s) on another thread will be applied at once, and KVO notifications will all be sent at once. Any intermediate steps are discarded, so if in the write transaction you incremented a property from one to ten, on the main thread you’ll get a single notification of a change directly from one to ten. Because properties can change in value when not in a write transaction or even as part of beginning a write transaction, trying to modify persisted Realm objects from within observeValueForKeyPath(_:ofObject:change:context:) is not recommended.
Unlike NSMutableArray properties, observing changes made to List properties does not require using mutableArrayValueForKey(_:), although that is supported for compatiblity with things not written for Realm. Instead, you can simply call the modification methods on List directly, and anyone observing the property it is stored in will be notified. List properties do not need to be marked as dynamic to be observable, unlike normal properties.
In our example apps you can find a short example of using Realm with ReactiveCocoa from Objective‑C, and ReactKit from Swift.
Migrations
When working with any database, it is likely your data model will change over time. Since data models in Realm are defined as standard Swift classes, making model changes is as easy as changing any other Swift class. For example, suppose we have the following Person model:
class Person: Object {
dynamic var firstName = ""
dynamic var lastName = ""
dynamic var age = 0
}We want to update the data model to require a fullName property, rather than separate first and last names. To do this, we simply change the object interface to the following:
class Person: Object {
dynamic var fullName = ""
dynamic var age = 0
}At this point if you had saved any data with the previous model version, there will be a mismatch between what Realm sees defined in code and the data Realm sees on disk. When this occurs, an exception will be thrown when you try to open the existing file unless you run a migration.
Performing a Migration
You define a migration and the associated schema version by setting Realm.Configuration.schemaVersion and Realm.Configuration.migrationBlock. Your migration block provides all the logic for converting data models from previous schemas to the new schema. When creating a Realm with this configuration, the migration block will be applied to update the Realm to the given schema version if a migration is needed.
For example, suppose we want to migrate the Person model declared earlier. The minimal necessary migration block would be the following:
// Inside your application(application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)
let config = Realm.Configuration(
// Set the new schema version. This must be greater than the previously used
// version (if you've never set a schema version before, the version is 0).
schemaVersion: 1,
// Set the block which will be called automatically when opening a Realm with
// a schema version lower than the one set above
migrationBlock: { migration, oldSchemaVersion in
// We haven’t migrated anything yet, so oldSchemaVersion == 0
if (oldSchemaVersion < 1) {
// Nothing to do!
// Realm will automatically detect new properties and removed properties
// And will update the schema on disk automatically
}
})
// Tell Realm to use this new configuration object for the default Realm
Realm.Configuration.defaultConfiguration = config
// Now that we've told Realm how to handle the schema change, opening the file
// will automatically perform the migration
let realm = try! Realm()At the very minimum all we need to do is to update the version with an empty block to indicate that the schema has been upgraded (automatically) by Realm.
While this is the minimum acceptable migration, we probably want to use this block to populate any new properties (in this case fullName) with something meaningful. Within the migration block we can call Migration().enumerate(_:_:) to enumerate each Object of a certain type, and apply any necessary migration logic. Notice how for each enumeration the existing Object instance is accessed via an oldObject variable and the updated instance is accessed via newObject:
// Inside your application(application:didFinishLaunchingWithOptions:)
Realm.Configuration.defaultConfiguration = Realm.Configuration(
schemaVersion: 1,
migrationBlock: { migration, oldSchemaVersion in
if (oldSchemaVersion < 1) {
// The enumerate(_:_:) method iterates
// over every Person object stored in the Realm file
migration.enumerate(Person.className()) { oldObject, newObject in
// combine name fields into a single field
let firstName = oldObject!["firstName"] as! String
let lastName = oldObject!["lastName"] as! String
newObject!["fullName"] = "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
}
})Once the migration is successfully completed, the Realm and all of its objects can be accessed as usual by your app.
Adding more versions
Suppose now we have two previous versions of the Person class:
// v0
// class Person: Object {
// dynamic var firstName = ""
// dynamic var firstName = ""
// dynamic var age = 0
// }
// v1
// class Person: Object {
// dynamic var fullName = "" // new property
// dynamic var age = 0
// }
// v2
class Person: Object {
dynamic var fullName = ""
dynamic var email = "" // new property
dynamic var age = 0
}The logic in our migration block might look like the following:
Realm.Configuration.defaultConfiguration = Realm.Configuration(
schemaVersion: 2,
migrationBlock: { migration, oldSchemaVersion in
// The enumerateObjects:block: method iterates
// over every 'Person' object stored in the Realm file
migration.enumerate(Person.className()) { oldObject, newObject in
// Add the `fullName` property only to Realms with a schema version of 0
if oldSchemaVersion < 1 {
let firstName = oldObject!["firstName"] as! String
let lastName = oldObject!["lastName"] as! String
newObject!["fullName"] = "\(firstName) \(lastName)"
}
// Add the `email` property to Realms with a schema version of 0 or 1
if oldSchemaVersion < 2 {
newObject!["email"] = ""
}
}
})
// Realm will automatically perform the migration and opening the Realm will succeed
let realm = try! Realm()For a more complete look at the implementation of a data schema migration, check out our migration sample app.
Linear Migrations
Suppose we have two users for our app: JP and Tim. JP updates the app very often, but Tim happens to skip a few versions. It’s likely that JP has seen every new version of our app, and every schema upgrade in sequence: he downloaded a version of the app that took him from v0 to v1, another update that took him from v1 to v2. In contrast, it’s possible that Tim will download an update of the app that would need to take him from v0 to v2 immediately. Structuring your migration blocks with non-nested if (oldSchemaVersion < X) calls ensures that they will see all necessary upgrades, no matter which schema version they start from.
Another scenario may arise in the case of users who skipped versions of your app. If you delete a property email at version 2 and re-introduce it at version 3, and a user jumps from version 1 to version 3, Realm will not be able to automatically detect the deletion of the email property, as there will be no mismatch between the schema on disk and the schema in the code for that property. This will lead to Tim’s Person object having a v3 address property that has the contents of the v1 address property. This may not be a problem, unless you changed the internal storage representation of that property between v1 and v3 (say, went from an ISO address representation to a custom one). To avoid this, we recommend you nil out the email property on the if (oldSchemaVersion < 3) statement, guaranteeing that all realms upgraded to version 3 will have a correct dataset.
Encryption
Realm’s encryption APIs are available for iOS, OS X & WatchKit but not watchOS because the <mach/mach.h> and <mach/exc.h> APIs used by Realm’s encryption mechanism are marked as __WATCHOS_PROHIBITED.
We’ve filed a radar about this issue: rdar://22063654.
Please take note of the Export Compliance section of our LICENSE, as it places restrictions against the usage of Realm if you are located in countries with an export restriction or embargo from the United States.
On iOS, it’s possible to encrypt Realm files with very little performance overhead by using NSFileProtection APIs. There are two main caveats to this approach: 1) the Realm file won’t be portable to other platforms (NSFileProtection is iOS-only) and 2) the Realm file won’t be encrypted on iOS devices that aren’t password-protected. To avoid these restrictions (or if you’re building an OS X app), then you should use Realm-level encryption.
Realm supports encrypting the database file on disk with AES-256+SHA2 by supplying a 64-byte encryption key when creating a Realm.
// Generate a random encryption key
let key = NSMutableData(length: 64)!
SecRandomCopyBytes(kSecRandomDefault, key.length,
UnsafeMutablePointer<UInt8>(key.mutableBytes))
// Open the encrypted Realm file
let config = Realm.Configuration(encryptionKey: key)
do {
let realm = try Realm(configuration: config)
// Use the Realm as normal
let dogs = realm.objects(Dog).filter("name contains 'Fido'")
} catch let error as NSError {
// If the encryption key is wrong, `error` will say that it's an invalid database
fatalError("Error opening realm: \(error)")
}This makes it so that all of the data stored on disk is transparently encrypted and decrypted with AES-256 as needed, and verified with a SHA-2 HMAC. The same encryption key must be supplied every time you obtain a Realm instance.
See our encryption sample app for an end-to-end app that generates an encryption key, stores it securely in the keychain, and uses it to encrypt a Realm.
There is a small performance hit (typically less than 10% slower) when using encrypted Realms.
Note that third party crash reporters (Crashlytics, PLCrashReporter etc.) should be registered before you first open an encrypted Realm, or you may get spurious reports of errors when the app didn’t actually crash.
Debugging
Debugging apps using Realm’s Swift API must be done through the LLDB console.
Note that although the LLDB script installed via our Xcode Plugin allows inspecting the contents of your Realm variables in Xcode’s UI, this doesn’t yet work for Swift. Instead, those variables will show incorrect data. You should instead use LLDB’s po command to inspect the contents of data stored in a Realm.
Debugging Encrypted Realms
Attaching an LLDB session to a process using an encrypted Realm is not currently supported. In some cases, you may work around this by setting REALM_DISABLE_ENCRYPTION=YES in your environment; this variable forces all encrypted API methods to work without encryption, allowing you to debug without having to change which Realm APIs you call in your app code. For obvious security reasons, this workaround will not work if you try to access an existing .realm file that was previously encrypted (this will result in an exception: File::AccessError), but it might be useful in cases where your app creates & accesses new Realm files.
Testing
Configuring the Default Realm
The easiest way to use and test Realm apps is to use the default realm. To avoid overriding application data or leaking state between tests, you can simply set the default Realm to a new file for each test.
import XCTest
// A base class which each of your Realm-using tests should inherit from rather
// than directly from XCTestCase
class TestCaseBase: XCTestCase {
override func setUp() {
super.setUp()
// Use an in-memory Realm identified by the name of the current test.
// This ensures that each test can't accidentally access or modify the data
// from other tests or the application itself, and because they're in-memory,
// there's nothing that needs to be cleaned up.
Realm.Configuration.defaultConfiguration.inMemoryIdentifier = self.name
}
}Injecting Realm Instances
Another way to test realm-related code is to have all the methods you’d like to test accept a Realm instance as an argument, so that you can pass in different realm when running the app and when testing it. For example, suppose your app has a method to GET a user profile from a JSON API and you’d like to test that the local profile is properly created:
// Application Code
func updateUserFromServer() {
let url = NSURL(string: "http://myapi.example.com/user")
NSURLSession.sharedSession().dataTaskWithURL(url!) { data, _, _ in
let realm = try! Realm()
createOrUpdateUserInRealm(realm, withData: data!)
}
}
public func createOrUpdateUserInRealm(realm: Realm, withData data: NSData) {
let object = try! NSJSONSerialization.JSONObjectWithData(data, options: [])
as! [String: String]
try! realm.write {
realm.create(User.self, value: object, update: true)
}
}
// Test Code
let testRealmPath = "..."
func testThatUserIsUpdatedFromServer() {
let config = Realm.Configuration(path: testRealmPath)
let testRealm = try! Realm(configuration: config)
let jsonData = "{\"email\": \"help@realm.io\"}"
.dataUsingEncoding(NSUTF8StringEncoding)!
createOrUpdateUserInRealm(testRealm, withData: jsonData)
let expectedUser = User()
expectedUser.email = "help@realm.io"
XCTAssertEqual(testRealm.objects(User).first!,
expectedUser,
"User was not properly updated from server.")
}Avoid Linking Realm and Tested Code in Test Targets
Since you’re using Realm as a dynamic framework, you’ll need to make sure your unit test target can find Realm. You can do this by adding the parent path to RealmSwift.framework to your unit test’s “Framework Search Paths”.
If your tests fail with an exception message "Object type '...' not persisted in Realm", it’s likely because you’ve linked the Realm framework directly to your test target, which should not be done. Unlinking Realm from your test target should address that.
You should also make sure to only compile your model class files in your application or framework targets; never add them to your unit test targets. Otherwise, those classes will be duplicated when testing, which can lead to difficult to debug issues (see this issue for details).
You’ll need to make sure all the code you need to test is exposed to your unit test targets (use the public access modifier in Swift 1.2, or @testable in Swift 2.0 and later).
REST APIs
Realm easily integrates with persisting data from REST API responses, providing several key benefits:
- Storing your REST data locally in Realm allows you to provide cached information, even when your device isn’t online, resulting in a nicer user experience.
- By preloading your dataset in Realm, you can take advantage of its lookup speed, being able to provide a better search and lookup experience than would be possible making the same query against a REST API.
- Storing your data locally with Realm can reduce server-side resource utilization by only needing to request data that has since changed since the last request.
Best Practices
- Asynchronous Requests — Network requests and other blocking operations should never be performed on the main thread, as that will block the UI from updating for an unacceptable amount of time. For that same reason, it is recommended that adding or updating a large number of objects in Realm are also kept off the main queue and performed in the background. You can take advantage of the Notifications feature of Realm to be automatically notified when the data has been comitted.
- Caching large datasets — We recommend you pre-fetch data when possible and store it locally in Realm. This allows you to perform queries over your entire dataset locally, taking full advantage of the speed benefits that Realm provides.
- Insert-or-update — If your dataset has a unique identifier, such as a primary key, you can use it to easily implement insert-or-update logic using
Realm().add(_:update:): with new information received from a REST API response. These methods automatically check if each object already exists and will accordingly either
Current Limitations
Realm is currently in beta and we are continuously adding features and fixing issues while working towards a 1.0 release. Until then, we’ve compiled a list of our most commonly hit limitations.
Please refer to our GitHub issues for a more comprehensive list of known issues.
General Limits
Realm aims to strike a balance between flexibility and performance. In order to accomplish this goal, realistic limits are imposed on various aspects of storing information in a realm. For example:
- Class names must be between 0 and 63 bytes in length. UTF8 characters are supported. An exception will be thrown at your app’s initialization if this limit is exceeded.
- Property names must be between 0 and 63 bytes in length. UTF8 characters are supported. An exception will be thrown at your app’s initialization if this limit is exceeded.
- NSData properties cannot hold data exceeding 16MB in size. To store larger amounts of data, either break it up into 16MB chunks or store it directly on the file system, storing paths to these files in the realm. An exception will be thrown at runtime if your app attempts to store more than 16MB in a single property.
- NSDate properties can only persist date information down to one second. Refer to the NSDate entry in Current Limitations below for more information.
- Any single Realm file cannot be larger than the amount of memory your application would be allowed to map in iOS — this changes per device, and depends on how fragmented the memory space is at that point in time (there is a radar open about this issue: rdar://17119975). If you need to store more data, you can map it over multiple Realm files.
Fine-grained notifications are not yet supported
While it is possible to receive notifications when a realm changes (see Notifications), it is not currently possible to determine what was added/removed/moved/updated from that notification. We will be adding this feature in the near future. Key-Value Observation can be used for per-object change notifications, including detecting when a specific object is deleted.
NSDate is truncated to the second
Persisting an NSDate with a fractional number of seconds will truncate the date to the second. A fix for this is in progress. See GitHub issue #875 for more details. In the meantime, you can store NSTimeInterval properties with no loss in precision.
Realm Object Setters & Getters cannot be overriden
Since Realm overrides setters and getters to back properties directly by the underlying database, you cannot override them on your objects. A simple workaround is to create new, realm-ignored properties, whose accessors can be overriden, and can call other setters/getters.
File size & tracking of intermediate versions
You should expect a Realm database to take less space on disk than an equivalent SQLite database. If your Realm file is much larger than you expect, it may be because you have a Realm that is referring to an older version of the data in the database.
In order to give you a consistent view of your data, Realm only updates the active version accessed at the start of a run loop iteration. This means that if you read some data from the Realm and then block the thread on a long-running operation while writing to the Realm on other threads, the version is never updated and Realm has to hold on to intermediate versions of the data which you may not actually need, resulting in the file size growing with each write. The extra space will eventually be reused by future writes, or may be compacted — for example by calling Realm().writeCopyToPath(_:encryptionKey:).
To avoid this issue you, may call invalidate to tell Realm that you no longer need any of the objects that you’ve read from the Realm so far, which frees us from tracking intermediate versions of those objects. The Realm will update to the latest version the next time it is accessed.
You may also see this problem when accessing Realm using Grand Central Dispatch. This can happen when a Realm ends up in a dispatch queue’s autorelease pool as those pools may not be drained for some time after executing your code. The intermediate versions of data in the Realm file cannot be reused until the Realm object is deallocated. To avoid this issue, you should use an explicit autorelease pool when accessing a Realm from a dispatch queue.
List and RealmOptional properties aren’t accessible from Objective‑C
If you need to access your Realm Swift models from Objective‑C, note that any List and RealmOptional properties will not be available (like any other Swift-only data type) - if necessary, you can add wrapper getter & setter methods convert to and from NSNumber or NSArray.
Additionally, versions of Xcode prior to 7 Beta 5 had a known Swift bug that would result in compiler errors due to an invalid auto-generated Objective‑C header (-Swift.h). The workaround is to make all your List and RealmOptional properties private or internal. See GitHub issue #1925 for more details.
FAQ
How big is the Realm library?
Once your app is built for release, Realm should only add around 1MB to its size. The releases we distribute are significantly larger because they include support for the iOS and watchOS simulators, some debug symbols, and bitcode, which are all stripped by Xcode automatically when you build your app.
Should I use Realm in production applications?
Realm has been used in production in commercial products since 2012.
You should expect our Objective‑C & Swift APIs to change as we evolve the product from community feedback — and you should expect more features & bugfixes to come along as well.
Do I have to pay to use Realm?
No, Realm is entirely free to use, even in commercial projects.
How do you all plan on making money?
We’re actually already generating revenue selling enterprise products and services around our technology. If you need more than what is currently in our releases or in realm-cocoa, we’re always happy to chat by email. Otherwise, we are committed to developing realm-cocoa in the open, and to keep it free and open-source under the Apache 2.0 license.
I see references to a “core” in the code, what is that?
The core is referring to our internal C++ storage engine. It is not currently open-source but we do plan on open-sourcing it also under the Apache 2.0 license once we’ve had a chance to clean it, rename it, and finalize major features inside of it. In the meantime, its binary releases are made available under the Realm Core (TightDB) Binary License.
I see a network call to Mixpanel when I run my app, what is that?
Realm collects anonymous analytics when your app is run with a debugger attached, or when it runs in a simulator. This is completely anonymous and helps us improve the product by flagging which versions of Realm, iOS, OS X, or which language you target and which versions we can deprecate support for. This call does not run when your app is in production, or running on your user’s devices — only from inside your simulator or when a debugger is attached. You can see exactly how & what we collect, as well as the rationale for it in our source code.
Troubleshooting
Crash Reporting
We encourage you to use a crash reporter in your application. Many Realm operations could potentially fail at runtime (like any other disk IO), so collecting crash reports from your application will help identify areas where either you (or us) can improve error handling and fix crashing bugs.
Most commercial crash reporters have the option of collecting logs. We strongly encourage you to enable this feature. Realm logs metadata information (but no user data) when throwing exceptions and in irrecoverable situations, and these messages can help debug when things go wrong.
Reporting Realm Issues
If you’ve found an issue with Realm, please either file an issue on GitHub or email us at help@realm.io with as much information as possible for us to understand and reproduce your issue.
The following information is very useful to us:
- Goals.
- Expected results.
- Actual results.
- Steps to reproduce.
- Code sample that highlights the issue (full Xcode projects that we can compile ourselves are ideal).
- Version of Realm / Xcode / OS X.
- Version of involved dependency manager (CocoaPods / Carthage).
- Platform, OS version & architecture on which the bug happens (e.g. 64-bit iOS 8.1).
- Crash logs & stack traces. See Crash Reporting above for details.